Angular Variables
Angular Variables: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Kinematics of Circular Motion, Angular Displacement, Linear Velocity in Circular Motion, Angular Velocity in Circular Motion, Relation between Linear and Angular Velocity, Angular Acceleration & Translational and Angular Acceleration etc.
Important Questions on Angular Variables
Two particles of mass M and m are moving in a circle of radii R and r. If their time – periods are same, what will be the ratio of their linear velocities?
What is the linear velocity if the angular velocity vector is and position vector is ?
A body is whirled in a horizontal circle of radius 20 cm. It has an angular velocity of What is its linear velocity at any point on circular path
When a body moves with a constant speed along a circle
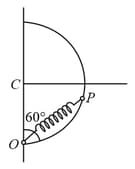
A smooth semicircular wire track of radius is fixed in a vertical plane. One end of a massless spring of natural length is attached to the lowest point of the wire track. A small ring of mass which can slide on the track is attached to the other end of the spring. The ring is held stationary at point such that the spring makes an angle of with the vertical. The spring constant . Consider the instant when the ring is released. The normal reaction on the ring by the track is
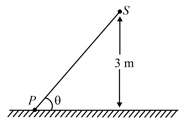
Spotlight rotates in a horizontal plane with a constant angular velocity of . The spot of light moves along the wall at a distance of . The velocity of the spot when (see. fig.) is
The angular acceleration of a body, moving along the circumference of a circle, is:
A merry-go-round rotates from rest with constant angular acceleration . Ratio of time to rotate first 2 revolutions and next 2 revolutions is
A particle is moving with constant speed in a circular path. When the particle turns by an angle the ratio of instantaneous velocity to its average velocity is The value of will be
A disc of radius rolls on a rough horizontal surface. The distance covered by the point A in one revolution is:
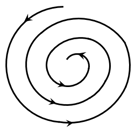
A particle is moving on a spiral path as shown in the figure. The speed of particle remains constant.
In circular motion speed depends on angular position as . The value of as a function of time is
Relation between angular acceleration and linear acceleration.
A phonograph turn-table rotating at slows down and stops in after the motor is turned off. Then the revolutions made by it in this time are
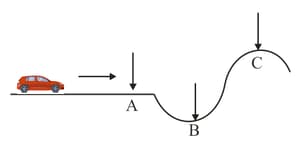
A car is running on a hilly road as shown in figure (side view). The friction between the wheels of the car and the road is constant and the car is moving at a constant speed. If the brakes are applied hard at any of the following points so that the wheels do not skid, then the value of the frictional force immediately after braking is maximum if the car is at
The speed of a particle in a circle is along the circumference of a circle of radius If the speed increases at the rate of . The acceleration of the particle at a given instant is
What is the angular acceleration of a particle in circular motion, which slows from to rest in ?
A body revolves with constant speed v in a circular path of radius r. The magnitude of its average acceleration during motion between two points in diametrically opposite direction is
In a car accelerates uniformly form rest to such a speed that its wheels are turning at a rate of . How many revolutions does the wheel turn?
A particle in UCM completes revolution in . The angular velocity of the particle is